
Calculus: Early Transcendentals, 11th Edition
By Howard Anton, Irl C. Bivens, Stephen Davis
Researchers and educators agree that it takes more than academic knowledge to be prepared for college—intrapersonal competencies like conscientiousness have been proven to be strong determinants of success. WileyPLUS with ORION for Calculushelps you identify students’ proficiency early in the semester and intervene as needed.
Schedule a Demo Sign Up for a Test Drive Adopt WileyPLUSWant to learn more about WileyPLUS? Click Here
New video program helps student see what they learn
Videos of worked examples and problems highlight specific learning objectives in the Single Variable chapters of the Eleventh Edition.
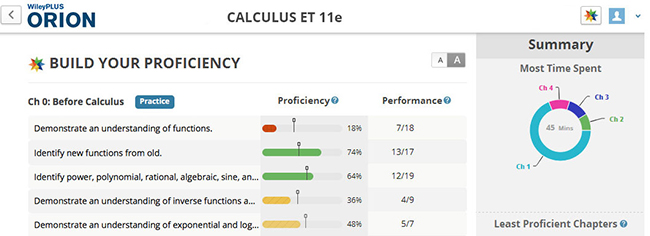
Students get the practice they need to master concepts
ORION Algebra and Trigonometry Refresher Module helps students master algebra, trigonometry, and polynomial equations. With ORION, students can create a personalized study plan and instructors can use class time to focus on Calculus.
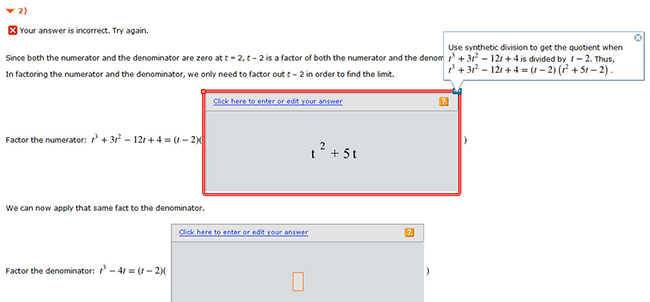
Students get feedback at the point of learning
New Answer-Specific Feedback Questions give students customized feedback on the actual work they’re doing at the point of learning.
What’s New
• WileyPLUS is a research-based online environment for effective teaching and learning. Interactive study tools and resources–including the complete online textbook–give students more value for their money.
• Industry-leading support from WileyPLUS with ORION: Resources and personal support are available from the first day of class onward through technical support; WileyPLUS account managers; WileyPLUS with QuickStart; and WileyPLUS Student Partner Program.
• Relevant student study tools and learning resources: Ensures positive learning outcomes including: graphing and math Palette tutorial videos; interactive illustrations; calculus applets; and student practice activities.
• Technology Exercises: In the textbook, these exercises—marked with an icon for easy identification—are designed to be solved using either a graphing calculator or a computer algebra system such as Mathematics, Maple, or Derive.
• Quick Check Exercises: Each exercise set begins with approximately five exercises (answers included) that are designed to provide student with an immediate assessment of whether they have mastered key ideas form the section.
• Career Preparation: This program has been created at a mathematical level that will prepare students for a wide variety of careers that require a sound mathematical background, including engineering, the various sciences, and business.
Howard Anton obtained his B.A. from Lehigh University, his M.A. from the University of Illinois, and his Ph.D. from the Polytechnic Institute of Brooklyn, all in mathematics. He worked in the manned space program at Cape Canaveral in the early 1960’s. In 1968 he became a research professor of mathematics at Drexel University in Philadelphia, where he taught and did mathematical research for 15 years. In 1983 he left Drexel as a Professor Emeritus of Mathematics to become a full-time writer of mathematical textbooks. There are now more than 150 versions of his books in print, including translations into Spanish, Arabic, Portuguese, French, German, Chinese, Japanese, Hebrew, Italian, and Indonesian. He was awarded a Textbook Excellence Award in 1994 by the Textbook Authors Association, and in 2011 that organization awarded his Elementary Linear Algebra text its McGuffey Award.
INTRODUCTION: The Roots of Calculus
1 LIMITS AND CONTINUITY
1.1 Limits (An Intuitive Approach)
1.2 Computing Limits
1.3 Limits at Infinity; End Behavior of a Function
1.4 Limits (Discussed More Rigorously)
1.5 Continuity
1.6 Continuity of Trigonometric Functions
1.7 Inverse Trigonometric Functions
1.8 Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
2 THE DERIVATIVE
2.1 Tangent Lines and Rates of Change
2.2 The Derivative Function
2.3 Introduction to Techniques of Differentiation
2.4 The Product and Quotient Rules
2.5 Derivatives of Trigonometric Functions
2.6 The Chain Rule
3 TOPICS IN DIFFERENTIATION
3.1 Implicit Differentiation
3.2 Derivatives of Logarithmic Functions
3.3 Derivatives of Exponential and Inverse Trigonometric Functions
3.4 Related Rates
3.5 Local Linear Approximation; Differentials
3.6 L’Hôpital’s Rule; Indeterminate Forms
4 THE DERIVATIVE IN GRAPHING AND APPLICATIONS
4.1 Analysis of Functions I: Increase, Decrease, and Concavity
4.2 Analysis of Functions II: Relative Extrema; Graphing Polynomials
4.3 Analysis of Functions III: Rational Functions, Cusps, and Vertical Tangents
4.4 Absolute Maxima and Minima
4.5 Applied Maximum and Minimum Problems
4.6 Rectilinear Motion
4.7 Newton’s Method
4.8 Rolle’s Theorem; Mean-Value Theorem
5 INTEGRATION
5.1 An Overview of the Area Problem
5.2 The Indefinite Integral
5.3 Integration by Substitution
5.4 The Definition of Area as a Limit; Sigma Notation
5.5 The Definite Integral
5.6 The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
5.7 Rectilinear Motion Revisited Using Integration
5.8 Average Value of a Function and its Applications
5.9 Evaluating Definite Integrals by Substitution
5.10 Logarithmic and Other Functions Defined by Integrals
6 APPLICATIONS OF THE DEFINITE INTEGRAL IN GEOMETRY, SCIENCE, AND ENGINEERING
6.1 Area Between Two Curves
6.2 Volumes by Slicing; Disks and Washers
6.3 Volumes by Cylindrical Shells
6.4 Length of a Plane Curve
6.5 Area of a Surface of Revolution
6.6 Work
6.7 Moments, Centers of Gravity, and Centroids
6.8 Fluid Pressure and Force
6.9 Hyperbolic Functions and Hanging Cables
7 PRINCIPLES OF INTEGRAL EVALUATION
7.1 An Overview of Integration Methods
7.2 Integration by Parts
7.3 Integrating Trigonometric Functions
7.4 Trigonometric Substitutions
7.5 Integrating Rational Functions by Partial Fractions
7.6 Using Computer Algebra Systems and Tables of Integrals
7.7 Numerical Integration; Simpson’s Rule
7.8 Improper Integrals
8 MATHEMATICAL MODELING WITH DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
8.1 Modeling with Differential Equations
8.2 Separation of Variables
8.3 Slope Fields; Euler’s Method
8.4 First-Order Differential Equations and Applications
9 INFINITE SERIES
9.1 Sequences
9.2 Monotone Sequences
9.3 Infinite Series
9.4 Convergence Tests
9.5 The Comparison, Ratio, and Root Tests
9.6 Alternating Series; Absolute and Conditional Convergence
9.7 Maclaurin and Taylor Polynomials
9.8 Maclaurin and Taylor Series; Power Series
9.9 Convergence of Taylor Series
9.10 Differentiating and Integrating Power Series; Modeling with Taylor Series
10 PARAMETRIC AND POLAR CURVES; CONIC SECTIONS
10.1 Parametric Equations; Tangent Lines and Arc Length for Parametric Curves
10.2 Polar Coordinates
10.3 Tangent Lines, Arc Length, and Area for Polar Curves
10.4 Conic Sections
10.5 Rotation of Axes; Second-Degree Equations
10.6 Conic Sections in Polar Coordinates
11 THREE-DIMENSIONAL SPACE; VECTORS
11.1 Rectangular Coordinates in 3-Space; Spheres; Cylindrical Surfaces
11.2 Vectors
11.3 Dot Product; Projections
11.4 Cross Product
11.5 Parametric Equations of Lines
11.6 Planes in 3-Space
11.7 Quadric Surfaces
11.8 Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinates
12 VECTOR-VALUED FUNCTIONS
12.1 Introduction to Vector-Valued Functions
12.2 Calculus of Vector-Valued Functions
12.3 Change of Parameter; Arc Length
12.4 Unit Tangent, Normal, and Binormal Vectors
12.5 Curvature
12.6 Motion Along a Curve
12.7 Kepler’s Laws of Planetary Motion
13 PARTIAL DERIVATIVES
13.1 Functions of Two or More Variables
13.2 Limits and Continuity
13.3 Partial Derivatives
13.4 Differentiability, Differentials, and Local Linearity
13.5 The Chain Rule
13.6 Directional Derivatives and Gradients
13.7 Tangent Planes and Normal Vectors
13.8 Maxima and Minima of Functions of Two Variables
13.9 Lagrange Multipliers
14 MULTIPLE INTEGRALS
14.1 Double Integrals
14.2 Double Integrals over Nonrectangular Regions
14.3 Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates
14.4 Surface Area; Parametric Surfaces
14.5 Triple Integrals
14.6 Triple Integrals in Cylindrical and Spherical Coordinates
14.7 Change of Variables in Multiple Integrals; Jacobians
14.8 Centers of Gravity Using Multiple Integrals
15 TOPICS IN VECTOR CALCULUS
15.1 Vector Fields
15.2 Line Integrals
15.3 Independence of Path; Conservative Vector Fields
15.4 Green’s Theorem
15.5 Surface Integrals
15.6 Applications of Surface Integrals; Flux
15.7 The Divergence Theorem
15.8 Stokes’ Theorem
APPENDICES
A TRIGONOMETRY SUMMARY
B FUNCTIONS (SUMMARY)
C NEW FUNCTIONS FROM OLD (SUMMARY)
D FAMILIES OF FUNCTIONS (SUMMARY)

